Dental surgery
of oral cavity. With regard to this area there are various surgical procedures to be performed in the interior of the mouth and in the adjacent area. Dental surgery is an independent specialty supporting other areas of dentistry, including endodontics (root canal), dental prosthetics, periodontology (also known as periodontics) and implantology.
The dental surgery can distinguish the following sections:
- Hard surgery – involves extracting (pulling teeth), hemisection (as amended by removing diseased portion of the tooth), resection (removal of the root apex), the correction side bone implants.
- Soft Surgery – treatments in periodontics (curettages closed and open treatments, lobar), correction of the gums and mucous membranes plastics, removing cysts and radicular tooth buds.
- Reconstructive surgery – guided bone regeneration (superstructure), raising the sinus nerve repositioning, filling bone defects.
- Traumatology – after accidents and mechanical trauma, involves smoothing the sharp edges of teeth, fillings, teeth stabilization.
Characteristics of the most commonly performed surgical procedures:
- Extraction (removal) of tooth by minimally invasive technique
- The treatment is carried out in preparation for the implant. Removal of a tooth takes place under anesthesia. During the procedure the dentist doesn’t use forcepts for formatted wound to be as small as possible. This allows the gums to heal faster.
- Hemisection
- Hemisection is the removal of a fragment of root of the tooth crown that was irreparably damaged. In many cases, a prosthetic filling of a cavity is a must.
- Plastic surgery of the frenulum
- Frenulum tissue is placed between the gum above the upper incisors and the rear of the upper lip. When the frenulum is too short it can cause the exposure of necks as a result of unfolding of facial movements. Therefore a simple procedure is carried out to undercut, which causes elongation frenulum.
- Resection
- Resection is a procedure which usually is dedicated for one root teeth (canines and incisors). Involves removing the root tip, which is used for chronic inflammatory changes. Often it is necessary to fill voids with biocompatible material.
- Resection of the multi root tooth
- Multi-root resection is a surgical procedure which purpose is to remove diseased, irreparably altered parts of the root apex in the tooth.
- Removal of impacted tooth
- Impacted tooth is one that because of lacks of space or improper placement could not grow properly. Generally after surgery the patient can not ingest food for several hours. It is recommended to eat something light before a visit.
- Tooth removal (extraction)
- Extraction involves the removal of a tooth from the socket using the appropriate tools such as tongs, fork, etc.
Geistlich Biomaterials – Biomaterials for Guided Bone Regeneration and Guided Tissue Regeneration
In the twenty-first century dentistry has as its main objective the aesthetics and functional restoration of lost teeth, and the preservation of endangered tooth extraction using modern methods of treatment. Treatment is possible through the use of appropriate materials, which not only enhance the already loose teeth or accelerate the regeneration of bone tissue, but also improves the anatomy of the alveolar process. Due to the specific properties of these materials are especially valuable in cases of planned prosthetic reconstruction using implants. Supplier of high quality materials and preparations for Guided Tissue Regeneration and Guided Tissue Regeneration is a Swiss company Geistlich Biomaterials.
When implanting implants functionality and aesthetics play a major role. Currently, the use of materials bone substitues and collagen membranes has become part of standard procedure for the treatment of bone defects. The structure of the material Geistlich Bio-Oss ® resembles human bone.
The process of natural regeneration of bone material Bio-Oss ®:
The structure of the matrix provides stabilization of a clot.
Revascularization.
The deposition of new bone structure and mineral conductive properties.
Bone remodeling and material Bio-Oss® with osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Are there alternatives to Geistlich Bio-Oss®?
Instead, the preparation is possible with the use of patient’s own bone. This implies, however, the need for a second surgery, thus greatly increasing the total cost due to the use of more anesthesia. In addition, the patient is exposed to an additional burden.
- Geistlich Bio-Oss®
- is a substitute natural material derived from bovine bone. Created by the removal of the organic structure of the bones, so it is only the structure of the bone without any inorganic and organic components of the bacteria.
Due to the high degree of porosity, morphology Geistlich Bio-Oss ® can accelerate the migration to the region of implantation osteocytes material and its crystal structure, identical to the patient’s natural bone structure, allowing the resorption.
- Geistlich Bio-Gide®
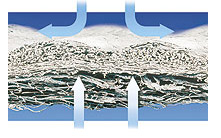
This is a restorable membrane reservoirs, composed of collagen fibers highly cleaned animal originated. It affects the acceleration of bone healing and mucosa (see figure): A / compacted layer of the mucosa to prevent ingrown B / porous layer makes it easy to integrate within the bone tissue. The creation of so-called firewall lets you block the proliferation of epithelial cells to the inside filled cavity. For this purpose, a membrane barrier is used. To not repeat treatment once more with a purpose to remove membrane after completion of regeneration, a technique was devoted to use resorbable membranes.
Dr. dentist Tomasz Gładysz
Specialist in Oral Surgery
Co-owner Unident Dental Center
Lecturer in the Department of Surgery at Jagiellonian University Medical Center
Senior Assistant in the Department of University Surgery Dental Clinic in Krakow